Dialog: Administer OPC UA Application
This dialog allows you to administer the OPC UA application. It contains settings and operations that enable the OPC UA application to coexist and communicate properly in the operating system and in the OPC UA ecosystem.
The "Administer OPC UA Application" dialog allows:
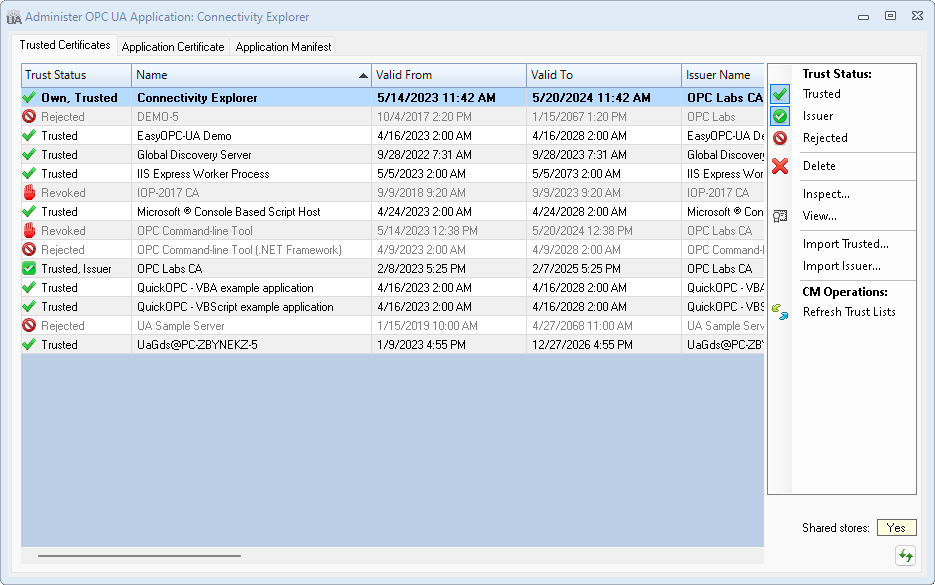
- Viewing and managing trusted certificates. The user can change the Trusted, issuer and Rejected states of the certificates, import certificates, and delete certificates.
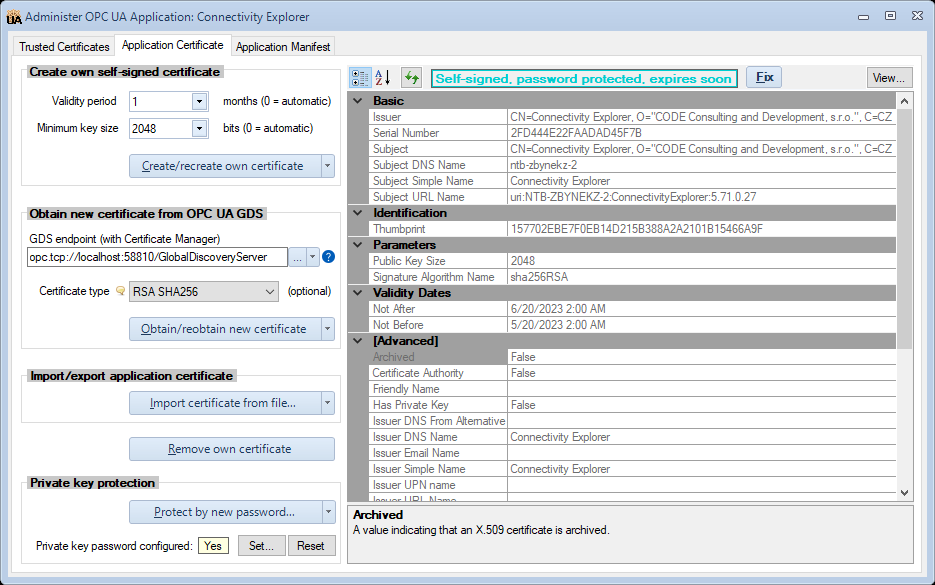
- Managing the own application certificate, either using self-signed approach, or from an OPC UA Global Discovery Server (GDS). The application certificate can be exported or imported. The user can also protect the private key of the certificate with a password, or unprotect it. Automatic fixes are offered for common issues with the application certificate.
- Viewing OPC UA application manifest.
The above listed aspects correspond to individual tabs on the dialog. If there is an important issue that needs your attention, the affected tab is displayed with an error or warning icon.
You can switch between the tabs as needed. When you are done with the dialog, press Esc or click the little cross icon in the upper right corner.
Trusted Certificates tab
Application Certificate tab
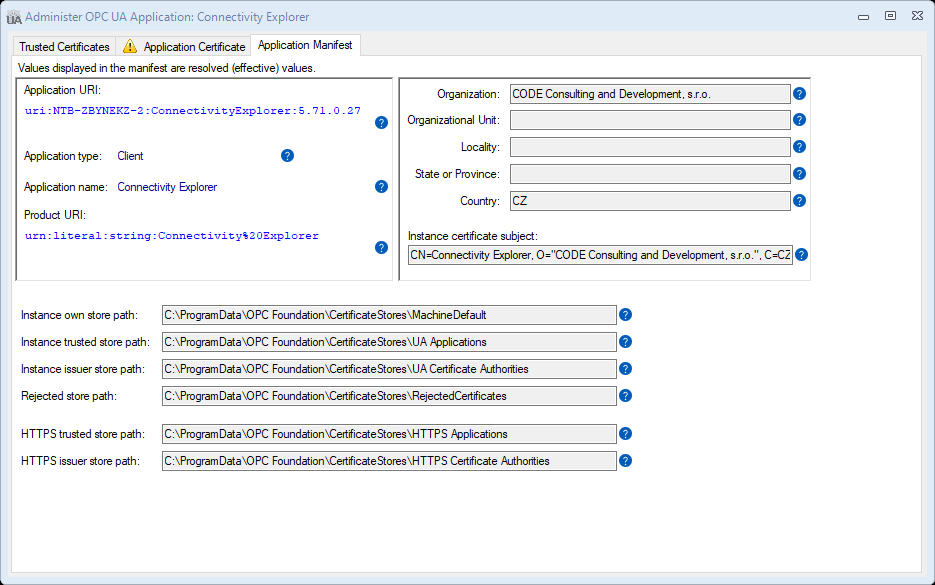
Application Manifest tab
The OPC UA application manifest contains the application registration information together with data related to PKI administration, such as paths to the certificate stores used.
The information contained in the OPC UA application manifest can roughly be divided into three areas:
- Information that identifies or otherwise integrates the application in the OPC UA ecosystem, such as application URI, application type, application name, and product URI.
- Information needed to create the application instance certificate, such as the certificate subject name or its parts. Note that the certificate also contains some of the information described above, such as the application URI.
- Information that allows the OPC UA application to execute and be administered in the operating system environment, such as location of the certificate stores it uses.
This logical separation is reflected in how the information is laid out on the Application Manifest tab:
You cannot change the information in the Application Manifest tab; it comes from the OPC UA application itself. Use this tab mainly to verify that the information displayed is correct, and/or to share it with other parties. For example, the application URI is needed in some scenarios to connect to the application.